Koch Brothers
Koch Brothers refers to Charles G. Koch and his brother David H. Koch, the billionaire co-owners of Koch Industries, one of the largest privately-held companies in the world.[1] The New Yorker has described David Koch and his brother Charles Koch as "longtime libertarians who believe in drastically lower personal and corporate taxes, minimal social services for the needy, and much less oversight of industry—especially environmental regulation."[2] The Kochs have built and bankrolled a powerful network of foundations, think tanks, and politically active organizations that try to influence elections and policy.
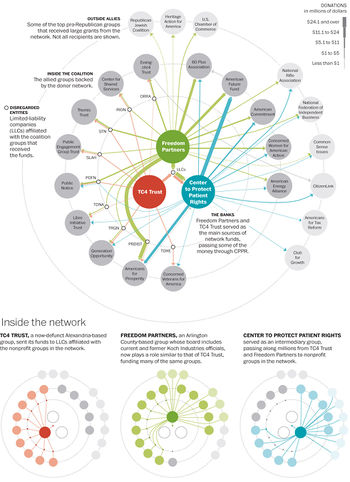
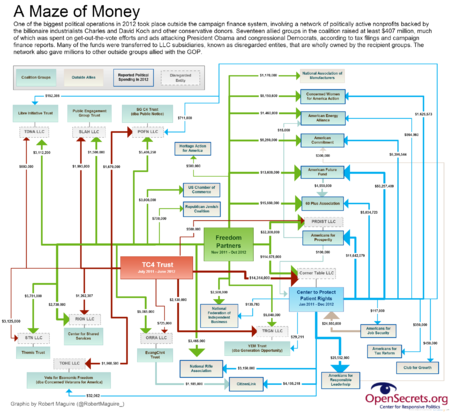
In the 2012 election cycle, the Kochs and fellow donors backed a "network of politically active nonprofit groups" that was "carefully constructed with extensive legal barriers to shield its donors," raising over $400 million for the election cycle, according to the Washington Post. As the Post explains, a "labyrinth of tax-exempt groups and limited-liability companies help[ed] mask the sources of the money, much of which went to voter mobilization and television ads attacking President Obama and congressional Democrats."[3]
The Koch brothers spent a total of $220 million on the 2014 midterm elections through their right-wing political advocacy groups: Americans for Prosperity and Freedom Partners.[4]
Together the Koch brothers were worth an estimated $102.4 billion as of May 2017.[5]
| Koch Wiki |
|---|
The Koch brothers -- David and Charles -- are the right-wing billionaire co-owners of Koch Industries. As two of the richest people in the world, they are key funders of the right-wing infrastructure, including the American Legislative Exchange Council (ALEC) and the State Policy Network (SPN). In SourceWatch, key articles on the Kochs include: Koch Brothers, Koch Industries, Americans for Prosperity, American Encore, and Freedom Partners. |
Contents
- 1 News and Controversies
- 1.1 Partnering with Marathon Oil to roll back car efficiency standard
- 1.2 "The Koch Brothers Are Killing Public Transit Projects Around the Country"
- 1.3 Koch Funded Dark Money Groups Investigated and Fined in California
- 1.4 Building a Post-Citizens United $400 Million Dark Money Web
- 1.5 Involvement in Scott Walker Race and Recall Election in 2010
- 2 Electoral Activity
- 3 Koch Brothers Early History
- 4 The Koch Fortune
- 5 Koch Brothers Early Activism, 1960-1980
- 6 Building the Koch Cadre, Non-Electoral Activity
- 7 Articles and Resources
News and Controversies
Partnering with Marathon Oil to roll back car efficiency standard
The Koch brothers played a pivotal role in the "covert campaign" to support President Trump's plan to "allow cars to emit more pollution," according to Dec. 2018 article in the New York Times. Marathon Petroleum "teamed up" with the American Legislative Exchange Council (ALEC), a Koch backed group. The Koch's are also a corporate sponsor of a bill "to repeal the corporate average fuel economy standards.” The times article also points to the Koch's support of the Heritage Foundation as part of the plan to reduce combat car efficiency regulations.[6]
"The Koch Brothers Are Killing Public Transit Projects Around the Country"
According to The New York Times via Americans for Prosperity (AFP), the Koch Brothers are "killing public transit projects around the country." Using data from i360 AFP activists are going to door in various cities urging their fellow citizens to oppose public transport plans. "The Kochs’ opposition to transit spending stems from their longstanding free-market, libertarian philosophy. It also dovetails with their financial interests, which benefit from automobiles and highways," The New York Times reported in June of 2018.[7]
Koch Funded Dark Money Groups Investigated and Fined in California
The Center to Protect Patient Rights, a group run by Koch operative Sean Noble, was fined by the California state elections board for violating campaign finance disclosure laws as part of a campaign to prohibit "unions from using automatic payroll deductions to raise money for political campaigns."[8]
Other "dark money" groups involved in the network included funding sources Freedom Partners and the TC4 Trust, CSE successor Americans for Prosperity, and a long list of Koch astroturf organizations like the 60 Plus Association, Generation Opportunity, American Commitment, Concerned Women for America, the Libre Initiative, and Public Notice.[9] Additional funding went to the Wisconsin Club for Growth, and from there to Citizens for a Strong America, both of which were later involved in a criminal investigation related to the 2012 election.[10]
Building a Post-Citizens United $400 Million Dark Money Web
According to the Washington Post, in 2012 the Kochs and fellow donors backed a "network of politically active nonprofit groups" that was "carefully constructed with extensive legal barriers to shield its donors," raising over $400 million for the election cycle. As the Post explains, a "labyrinth of tax-exempt groups and limited-liability companies help[ed] mask the sources of the money, much of which went to voter mobilization and television ads attacking President Obama and congressional Democrats."[3]
For example, Freedom Partners, which Politico has referred to as "the Koch brothers' secret bank", spent some $250 million in the 2012 election cycle, much of it spent in grants to other groups that ran so-called "issue ads" during the election.[11]
Involvement in Scott Walker Race and Recall Election in 2010
Walker's gubernatorial campaign received $43,000 from the Koch Industries PAC during the 2010 election. The Koch PAC gave $1 million to the Republican Governors Association, which in turn spent $65,000 on independent expenditures to support Walker.[12] The RGA also spent $3.4 million on TV ads and mailers attacking Walker's opponent, Milwaukee Mayor Tom Barrett. [13]
In a February 2012 interview with the Palm Beach Post, David Koch admitted that he was helping fund Wisconsin Gov. Scott Walker as Walker fought off a recall election sparked by his anti-union legislation.[14] The paper reported that Koch acknowledged his group, Americans for Prosperity, was "hard at work in places such as Wisconsin, where Gov. Scott Walker is facing off with public unions and grappling with a likely recall."[14]
Koch was quoted as saying, "We're helping him, as we should. We've gotten pretty good at this over the years [...] We've spent a lot of money in Wisconsin. We're going to spend more." [14]
Highlighting the recall as a fight against unions, Koch also stated that "What Scott Walker is doing with the public unions in Wisconsin is critically important. He's an impressive guy and he's very courageous…If the unions win the recall, there will be no stopping union power."[14]
Electoral Activity
2018 Election Cycle
The Koch brothers political network will spend between $300 and $400 million during the 2018 election cycle.[15] "The funds will be spread across a constellation of groups, including Americans for Prosperity and Freedom Partners Action Fund, along with Concerned Veterans for America, the Libre Initiative and Generation Opportunity, which now operate under the AFP banner," the Washington Post reported.[15]
2016 Election Cycle
The Koch brothers set a spending goal of $889 million for the 2016 election cycle.[16] In 2015, the Kochs spent $400 million, according to The Hill.[17] However, following the election, the Koch network reported spending $250 million in the 2016 election.[15] Not only do these numbers not add up, it is unclear if these numbers include the money to i360, the money given through KochPAC, or the money given personally by the Koch brothers to candidates or campaigns directly.
Koch-Funded Group Attacks Kasich in New Hampshire
The Koch-tied American Future Fund took out TV ads in New Hampshire against 2016 Republican Presidential Nominee John Kasich prior to the primary held on February 9, 2015.[18] In the ad, the group attacks Kasich's record for not being conservative enough, "John Kasich — not a conservative. Not even a moderate. An Obama Republican."[18] Nick Ryan, the current president of American Future Fund told The New York Times in an email that the group was running the ads because Kasich was "misleading New Hampshire voters" and that the “The real John Kasich record looks like something you might expect from a liberal politician like Barack Obama."[19]
Kasich finished second in the New Hampshire primary to Donald Trump.[20]
Koch-Backed American Future Fund Targets Presidential Candidate Ted Cruz in Iowa and South Carolina
American Future Fund, a Koch-funded entity located in Iowa, has taken out $1.5 million in ads against Cruz in South Carolina following the group's campaign ads against him in Iowa.[21] The TV ad criticizes Cruz for being "weak" on national security and for supporting a legal status for undocumented migrants in the US.[22] The narrator in the ad states that, “Cruz proposed mass legalization of illegal immigrants. He even praised the traitor Edward Snowden. Ted Cruz’s talk is cheap. His national security record is weak."[22]
2014 Election Cycle
Through their Americans for Prosperity group, the Koch brothers ran more than 34,000 television ads in the 2014 election cycle.[23] They also operated a network of workers on the ground in 35 states to mobilize voters to advance their political agenda.[23]
The Koch brothers spent a total of $220 million on the 2014 midterm elections through their right-wing political advocacy groups: Americans for Prosperity and Freedom Partners.[24]
Future Commitment to Politics
In a 2014 interview with the Wichita Business Journal, Charles Koch identified "cronyism" as one of the biggest problems facing the United States, adding, "You name it, in every industry we have this. The successful companies try to keep the new entrants down. Now that’s great for a company like ours. We make more money that way because we have less competition and less innovation. But for the country as a whole, it’s horrible."[25]
When asked why he continues to be involved in politics, despite negative public reactions, Charles answered, "It’s like Lee Trevino used to say, somebody asked him, "How are you winning all these golf tournaments?" and he said, “Well somebody has got to win them and it might as well be me.” That’s the way I am on this. There doesn’t seem to be any other large company trying to do this so it might as well be us. Somebody has got to work to save the country and preserve a system of opportunity."[25]
2012 Election Cycle
In the 2012 Election cycle, which President Obama was up for reelection and the democrat's majority in the Senate was challenged, the Koch brothers spent almost $400 million to advance their interests.[16]
According to Politico, after this network "spent hundreds of millions to win the White House and the Senate — and came up empty," the Kochs undertook a major audit of their organizations. Reportedly disappointed with the election results, Charles Koch wrote an e-mail to major donors about the need "to re-examine our vision and the strategies and capabilities required for success," adding that "Our goal of advancing a free and prosperous America is even more difficult than we envisioned, but it is essential that we continue, rather than abandon, this struggle."[26]
The Koch Donor Network
Since at least 2006, the Kochs have hosted semi-annual meetings for wealthy right-wing donors.[27] While these Koch network gatherings are carefully guarded, occasional leaked documents and recordings have revealed that they include "titans of industry — from health insurance companies, oil executives, Wall Street investors, and real estate tycoons — working together with conservative journalists and Republican operatives," as well as prominent public officials, including members of Congress, state governors, and even Supreme Court Justices Clarence Thomas and Antonin Scalia.[28] The meetings involve fundraising, reportedly in the millions of dollars, as well as discussions about political strategy.[29]
A full list of known participants in Koch summit meetings can be accessed on the Koch network page.
"Triad" Campaign Finance Scheme Avoids Disclosure Laws, 1996
The Koch’s have a long history of funding money into electoral campaigns. For example, the Kochs used a variety of means to influence the 1996 election cycle.
In Kansas, according to the Lawrence Journal-World,
- "Koch-linked contributions of ‘hard money’—gifts of more than $200 by identifiable individuals or political action committees divulged to the FEC—to the state's four representatives and two Senators totaled $130,600."[30]
Senate Democrats found evidence of more complex funding schemes, as well, namely a political campaign operation called "Triad," which they suggested "allowed wealthy individuals to put more money into the election process than they would otherwise legally have been allowed to do" while evading campaign reporting requirements.[31] In 1997, investigators for the Senate Governmental Affairs Committee told the New York Times that "they believe[d] Koch Industries support[ed] the Economic Education Trust, based in Twin Falls, Idaho, which gave $1.3 million to Triad in 1996."[32]
In an interview with Bill Moyers, staffer Beth Stein explained the scheme as follows:
- "One of the things that Triad did was set up two shell corporations, essentially, tax-exempt organizations. One was called Citizens for Reform and the other was called Citizens for the Republic Education Fund, and the sole thing that those corporations did was to air attack advertising in various races across the country."[33]
In 1998, the Minneapolis Star Tribute reported that “Koch Industries Inc. backed a secret trust that donated $1.8 million in 1996 to finance issue ads sympathetic to conservative Congressional candidates, [lending] new credence to the conclusion last year of Senate Democratic investigators that Koch's owners, Charles and David Koch, were probably the financiers behind the trust that contributed to at least two nonprofit groups.”[34]
Read the documents from the 1997 Senate Judiciary Committee investigation of "Illegal or Improper Activities in Connection With 1996 Federal Election Campaigns;" Triad is primarily discussed in Volumes 3-5.
Koch Brothers Early History
Charles Koch (b. 1935) and David Koch (b. 1940) are two of the four children of Fred Koch and Mary Koch. Fred Koch founded Wood River Oil and Refining Co. in 1940; it had been renamed Rock Island Oil & Refining Co. by 1961 and was renamed Koch Industries by Charles Koch in 1967.[35] Fred Koch was also a founder and executive committee member of the far-right John Birch Society, known for opposing the Civil Rights Act, the Voting Rights Act and communism.[31]
The senior Koch's views are thought to have influenced the Koch brothers' pro-business, anti-union agenda. Lisa Graves noted that "The Kochs' mistrust of public education can be traced to their father, Fred, who declared that the National Education Association was a communist group and public-school books were filled with “communist propaganda,” paranoia that extended to all unions, President Eisenhower and the “pro-communist” Supreme Court."[36] Echoing this anti-union fervor, David Koch has stated that Wisconsin Governor Scott Walker's attack on public unions was “critically important."[37]
He also accused President Barack Obama of being "a hardcore socialist."[38]
Relationship to John Birch Society
Fred Koch was a founding member of the John Birch Society. In the 1960s, Charles Koch opened a John Birch Society bookstore with Bob Love, a friend of his father.[39] At the time, the Society was campaigning against the civil rights movement, calling for the impeachment of Chief Justice Earl Warren, who had ordered public school desegregation in Brown v. Board of Education, and accusing President John F. Kennedy of "treason" in ads shortly before his assassination. [31]
Charles and Love didn't resign from the Society until 1968. The split was reportedly due to disagreement's about the Society's support for the Vietnam War.[31]
Charles shared his isolationist position with Robert LeFevre's all-white "Freedom School," which he funded and on whose board he sat. Charles had also encouraged his brother, David, to attend a Freedom School retreat, according to Sons of Wichita.[39]
The Koch Fortune
Charles Koch took over his father's Rock Island Oil and Refinery Company, becoming president and chairman in 1967 and renaming it Koch Industries [31] Since then, the company's revenues grew from just over $100 million to over $115 billion in 2014. The Koch brothers' fortunes have also grown dramatically in that time, increasing from $375 million each in 1984 to some $17 billion each in 2008--and a staggering $41 billion each in 2014, just a few years after the 2008 economic crisis.
In addition to successful investments and expansion of its resource extraction operations over the years, Koch Industries has engaged in commodity speculation and created new types of derivatives.[40] The Nation has reported that Koch Industries was "among the largest traders (including Goldman Sachs and Morgan Stanley) speculating on the price of oil in the summer of 2008,"[41] afterwards also playing a prominent role in lobbying against regulation of the derivatives market, according to Bloomberg Businessweek.[42]
Koch Industries has been involved in many investigations and indictments related to the Clean Air Act and the Clean Water Act.
A list of lawsuits involving Koch Industries can be accessed here: Legal Complaints Against Koch Industries
Koch Brothers Early Activism, 1960-1980
David Koch Runs for Vice President as Libertarian, 1980
David Koch was the vice-presidential nominee for the Libertarian Party in 1980, running alongside presidential candidate Ed Clark. About the failed bid, the New York Times has written that "much of what occurred in that quixotic campaign shaped what the Kochs have become today — a formidable political and ideological force determined to remake American politics, driven by opposition to government power and hostility to restrictions on money in campaigns."[43]
David Koch's campaign was made possible by Buckley v. Valeo, a 1976 Supreme Court decision that loosened campaign finance laws. The decision permitted unlimited spending of a candidate's own money on his/her own campaign, as well as unlimited spending by individuals to promote a candidate, if that individual was not coordinating their campaign with the candidate.[43] In 1979, David Koch wrote a letter to Libertarian Party members about his plan to make use this new loophole to fund a Libertarian Party campaign. “As the Vice presidential nominee of the Libertarian Party I will contribute several hundred thousand dollars to the Presidential campaign committee in order to ensure that our ideas and our Presidential nominee receive as much media exposure as possible.”[43] David would spend about $2.1 million on the campaign, but the Libertarian Party won just over 1% of the vote nationally.[43]
According to William Koch, Charles and David's brother, Charles began spending significantly on the Libertarian Party. According to the New York Times, William said in a 1986 interview, "Charles was giving as much to the Libertarians as he was paying out in dividends […] Pretty soon we would get the reputation that the company and the Kochs were crazy.”[43]
Statements David Koch made during the campaign are revealing of his anti-government views. As the New York Times reported about his statement at the 1979 Libertarian nominating convention, David "denounced the 'harassment of Koch Industries and implored the Libertarian Party activists to make the party 'a force that will roll back the coercive force of government.'"[43] At a speech on the campaign trail in 1980, "David Koch railed against what he saw as overregulation. Presidents Nixon and Carter had bequeathed an 'Alice in Wonderland' energy policy, he argued, a mix of subsidies and price controls that had stymied market forces and caused high prices and shortages."[43]
Charles Koch Calls for the Development of a “Well Financed Cadre”
Charles Koch began funding the Institute for Humane Studies in the 1960s. He also created his own Charles Koch Foundation to funnel money to the Libertarian Society. He helped found the Cato Institute in 1974, by which time he was already giving money to the Libertarian Party. Charles also purchased the Libertarian Review.[31]
In a 1974 speech, Charles Koch stated:
- "The important strategic consideration to keep in mind is that any program adopted should be highly leveraged so that we reach those whose influence on others produces a multiplier effect. That is why education programs are superior to political action, and support of talented free-market scholars is preferable to mass advertising. The development of a well financed cadre of sound proponents of the free enterprise philosophy is the most critical need facing us at the moment."[43]
The Kochs have funded a number of nonprofit organizations like the American Legislative Exchange Council, think tanks and legal foundations, which are listed here:
Building the Koch Cadre, Non-Electoral Activity
After the failed 1980 campaign for the vice presidency, the Koch brothers lessened their involvement in the Libertarian Party, increasingly focusing their attention and financial support on developing their own network of "educational programs" and "cadre" of free-market advocates.[43]
The Kochs' funding founded Citizens for a Sound Economy (CSE) in 1984, headed by Richard Fink. Fink was shortly thereafter appointed to President Ronald Reagan's "Commission on Privatization."[44] In the late 1980s and 1990s, CSE pushed for banking deregulation, like the elimination of Glass Steagall,[36] spearheaded the defeat of a greenhouse gas tax,[2] and helped in the defeat of health care reform in the Clinton era.[45][46]
In 2003, a rift between CSE and its related foundation led the Kochs to found Americans for Prosperity.[2] David Koch chairs the board of directors for the Americans for Prosperity Foundation.[47]
Today the brothers directly and indirectly fund a wide network of organizations that promote their "free enterprise philosophy," from think tanks to scholarship programs to policy advocacy groups. Recipients include a long list of academic institutions; Koch family foundations gave some $30.5 million to 221 colleges and universities from 2007 to 2012.[43]
Charles Lewis, the founder of the Center for Public Integrity, a nonpartisan watchdog group, said, “The Kochs are on a whole different level. There’s no one else who has spent this much money. The sheer dimension of it is what sets them apart. They have a pattern of lawbreaking, political manipulation, and obfuscation. I’ve been in Washington since Watergate, and I’ve never seen anything like it. They are the Standard Oil of our times.”[2]
Access a list of organizations with ties to the Koch brothers here.
Bankrolling American Legislative Exchange Council (ALEC)
Koch Industries has had a seat and a vote on the corporate board of the American Legislative Exchange Council (ALEC) since 1994. ALEC has awarded both Koch brothers its Adam Smith Free Enterprise Award.[36] The Nation reports that the Kochs have likely given over $1 million to ALEC over the years, and many of ALEC's model bills reflect the policies the Kochs have been advocating for decades.[36]
Funding Judicial Junkets
The Kochs have funded seminars for judges since the 1990s, first at the University of Kansas and later at George Mason University, which hosts the Koch-funded think tank the Mercatus Center. For example, the George Mason University Law & Economics Center hosted "an expenses-paid conference on public pension reform" which was funded by the Charles G. Koch Foundation, as well as corporate funders like ExxonMobil, Google, and Walmart, according to the Center for Public Integrity.[48] The Judicial Conference of the United States has noted that judges' attendance at such seminars "poses certain concerns," including that "judges may be influenced inappropriately by those who sponsor or contribute (financially or otherwise) to these seminar programs and who might be litigants before those judges."[49]
A report by Center for Media and Democracy/The Progressive found that a federal judge who halted an investigation into alleged illegal campaign coordination, which involved groups like the Wisconsin Club for Growth and Americans for Prosperity, "attended privately-funded, all-expenses-paid judicial seminars put on by George Mason University in 2006, 2008, 2010 and 2012."[50] The Washington Post reported on a similar conference in 2011, when Google was facing an antitrust investigation, writing that "Google executives worked behind the scenes with officials at George Mason University’s Law & Economics Center to put on academic conferences that would be attended by officials who were considering the case."[51]
Bankrolling the Tea Party
The Koch brothers and their network have played a significant role in supporting the far-right Tea Party movement. According to the New Yorker, the Kochs' "Americans for Prosperity has worked closely with the Tea Party since the movement’s inception," providing everything from "Tea Party talking points" to lists of officials for activists to contact to funding conferences.[2] The New York Times reported that Freedom Partners, for which "longtime Koch employees" constitute a majority of the board, has given grants to a number of Tea Party-affiliated groups.[52]
According to the New Yorker, a Koch Industries spokesperson has denied that the Kochs provide funding for Tea Party groups, and David Koch has told New York magazine, "No one representing the tea party has ever even approached me."[2]
Affiliated Groups
Prominent groups the Koch Brothers have funded include:
- Americans for Prosperity
- American Encore
- Freedom Partners
- Koch Family Foundations
- Cato Institute
- Heritage Foundation
- Mercatus Center at George Mason University
- Institute for Humane Studies
- Bill of Rights Institute
- American Future Fund
- Aegis Strategic
- Stand Together
- Freedom Partners Institute, Inc.
- i360
Articles and Resources
See the related articles below for more information on the Kochs.
Related SourceWatch Articles
- Koch Brothers
- Koch Family Foundations
- Americans for Prosperity
- Freedom Partners
- Cato Institute
- Heritage Foundation
- Koch Universities
- Koch Network
- Knowledge and Progress Fund
- American Encore
- DonorsTrust
- Donors Capital
- 60 Plus
- Generation Opportunity
- TC4 Trust
- Center to Protect Patient Rights
- American Future Fund
- Themis
- i360
- Public Notice
- The LIBRE Initiative
- American Legislative Exchange Council
- National Rifle Association
- U.S. Chamber of Commerce
- American Energy Alliance
- Front groups
- Propaganda
Related PRWatch Articles
- Nick Surgey, Revealed: Extensive Koch Links to New Right-Wing $250 Million Mega Fund, PRWatch, September 16, 2013.
- Brendan Fischer, California Elections Board Peels Back Layer of Dark Money Onion, Finds More Onion, PRWatch, November 6, 2012.
- Lisa Graves, ALEC Exposed: The Koch Connection, PRWatch, July 20, 2011.
External Articles
- Theda Skocpol and Alexander Hertel-Fernandez, THE KOCH EFFECT: The Impact of a Cadre-Led Network on American Politics, Prepared for presentation at the Inequality Mini-Conference, Southern Political Science Association San Juan, Puerto Rico", January 8, 2016.
- Theda Skocpol, Making Sense of the Koch Network, Scholar Strategy Network, October 2015.
- Bernie Sanders, What Do the Koch Brothers Really Want?, Common Dreams, April 11, 2014.
- Mike Allen and Jim Vandehei, Exclusive: The Koch brothers' secret bank, Politico, September 11, 2013.
- Eric Lach, Revealed: The Secret Koch Group That Gave Conservatives $236 Million In 2012, Talking Points Memo "TPM Muckracker," September 12, 2013.
- Kenneth P. Vogel, Koch World reboots, Politico, February 20, 2013.
- Kenneth P. Vogel and Tarini Parti, Inside Koch world, Politico, June 15, 2012.
- Asjylyn Loder and David Evans, Koch Brothers Flout Law Getting Richer With Secret Iran Sales, Bloomberg, October 3, 2011.
- Tony Carrk, The Koch Brothers: What You Need to Know About the Financiers of the Radical Right, Center for American Progress, April 2011.
- Jason Easley, Getting Rich Off The Poor: How The Koch Brothers Wealth Grew 43% Since 2010, PoliticusUSA, September 21, 2011.
- Brad Johnson, Forbes: Koch Brothers Now Worth $50 Billion, TruthOut, September 22, 2011.
References
- ↑ Forbes.com America's Largest Private Companies- Koch Industries, accessed July 2, 2014.
- ↑ Jump up to: 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 Jane Mayer, "Covert Operations," New Yorker, August 30, 2010. Accessed July 2, 2014.
- ↑ Jump up to: 3.0 3.1 Matea Gold, "Koch-backed political network, built to shield donors, raised $400 million in 2012 elections," Washington Post, January 5, 2013. Accessed June 30, 2014.
- ↑ Rebecca Ballhaus, Koch Brothers Nonprofits’ Spending Surged in 2014, Wall Street Journal, November 18, 2015.
- ↑ Lianna Brinded, The 33 richest people on earth, Business Insider, May 7, 2017.
- ↑ Hiroko Tabuchi The Oil Industry’s Covert Campaign to Rewrite American Car Emissions Rules The New York Times Dec 13, 2018
- ↑ Hiroko Tabuchi [https://www.nytimes.com/2018/06/19/climate/koch-brothers-public-transit.html?action=click&module=RelatedLinks&pgtype=Article How the Koch Brothers Are Killing Public Transit Projects Around the Country] The New York Times June 19, 2018
- ↑ Nicholas Confessore, "Group Linked to Kochs Admits to Campaign Finance Violations," New York Times, October 24, 2013. Accessed June 30, 2014.
- ↑ Al Shaw, Theodoric Meyer and Kim Barker, "How Dark Money Flows Through the Koch Network," ProPublica, February 14, 2014. Accessed June 30, 2014.
- ↑ Brendan Fischer, "WI Club for Growth, Target of Walker Recall Probe, at Center of Dark Money Web", Center for Media and Democracy, November 18, 2013. Accessed June 30, 2014.
- ↑ Mike Allen and Jim Vandehei, "Exclusive: The Koch brothers' secret bank," Politico, September 13, 2013. Accessed June 30, 2014.
- ↑ Lisa Graves, "A CMD Special Report: Scott Walker Runs on Koch Money," Center for Media and Democracy, February 18, 2011. Accessed July 7, 2014.
- ↑ Andy Kroll, "Wisconsin Gov. Scott Walker: Funded by the Koch Bros.," Mother Jones, February 18, 2011. Accessed July 7, 2014.
- ↑ Jump up to: 14.0 14.1 14.2 14.3 Stacy Singer, David Koch intends to cure cancer in his lifetime and remake American politics, Palm Beach Post, February 18, 2012.
- ↑ Jump up to: 15.0 15.1 15.2 James Hohmann and Matea Gold, Koch network to spend $300 million to $400 million on politics, policy in 2018 cycle, Washington Post, January 28, 2017.
- ↑ Jump up to: 16.0 16.1 Nicholas Confessore, Koch Brothers’ Budget of $889 Million for 2016 Is on Par With Both Parties’ Spending, New York Times, January 26, 2015.
- ↑ Jonathan Swan, Koch brothers network ready to oppose Trump, The Hill, February 1, 2016.
- ↑ Jump up to: 18.0 18.1 Cindy Zuvich, Koch-linked group blasts Kasich in ad buy, The Center for Public Integrity, January 28, 2016.
- ↑ Alexander Burns, John Kasich Is Called an ‘Obama Republican’ in New Hampshire Ads, The New York Times, January 27, 2016.
- ↑ The Washington Post, New Hampshire primary election results, The Washington Post, 2016.
- ↑ Alex Altman, Cruz Takes Fire on South Carolina Airwaves, Time, February 12, 2016.
- ↑ Jump up to: 22.0 22.1 Nick Gass, Cruz campaign asks stations to stop airing anti-Cruz ad, Politico, February 16, 2016.
- ↑ Jump up to: 23.0 23.1 Peter Overby, This Political Ad Was Paid For By — Oh, Never Mind, NPR, October 22, 2014.
- ↑ Rebecca Ballhaus, Koch Brothers Nonprofits’ Spending Surged in 2014, Wall Street Journal, November 18, 2015.
- ↑ Jump up to: 25.0 25.1 Daniel McCoy, "Charles Koch: business giant, bogeyman, benefactor and elusive (until now) -- exclusive interview," Wichita Business Journal, February 28, 2014. Accessed June 2, 2014.
- ↑ Ken Vogel, "Koch World reboots," Politico, February 20, 2013. Accessed June 30, 2014.
- ↑ Stephen Moore, "Private Enterprise," Wall Street Journal, May 6, 2006.
- ↑ Lee Fang, "MEMO: Health Insurance, Banking, Oil Industries Met With Koch, Chamber, Glenn Beck To Plot 2010 Election," ThinkProgress, October 20, 2010. Accessed June 30, 2010.
- ↑ Lee Fang, "EXCLUSIVE: Koch Brothers Convene Ultra-Secret Billionaires Meeting To Raise Funds, Plot Strategy," Republic Report, February 3, 2012. Accessed June 30, 2014.
- ↑ Tim Carpenter, "Koch Industries Flexes Political Muscle in Kansas," Lawrence Journal-World, November 16, 1997. Accessed July 7, 2014.
- ↑ Jump up to: 31.0 31.1 31.2 31.3 31.4 31.5 Lisa Graves, "The Koch Cartel: Their Reach, Their Reactionary Agenda, and Their Record," The Progressive, July/August 2014.
- ↑ Leslie Wayne, "Papers Link Donations to 2 On Senate Hearings Panel," New York Times, October 30, 1997. Accessed June 30, 2014.
- ↑ Frontline, PBC "Washington's Other Scandal," show transcript, air date October 6, 1998. Accessed June 30, 2014.
- ↑ Greg Gordon, "Koch backed GOP ads in '96 races, report confirms; The company's owners funded a trust that gave $ 1.8 million to boost conservative candidates." Star Tribune (Minneapolis), June 2, 1998, Metro Edition. Pg. 5A.
- ↑ Fred and Mary Koch Foundation, History, organizational website, accessed June 30, 2014.
- ↑ Jump up to: 36.0 36.1 36.2 36.3 Lisa Graves, "ALEC Exposed: The Koch Connection," The Nation, July 2012, 2011. Accessed June 2, 2014.
- ↑ Mary Bottari, "On Anniversary of Prank Call the Real David Koch Wants to "Stop Union Power" in Wisconsin," PR Watch, February 21, 2012.
- ↑ Sarah Owen, "David Koch Gives President Obama Zero Credit for Bin Laden’s Death," New York Magazine, May 5, 2011.
- ↑ Jump up to: 39.0 39.1 Daniel Schulman, Sons of Wichita: How the Koch Brothers Became America's Most Powerful and Private Dynasty, Grand Central Publishing, 2014.
- ↑ Lee Fang, "How Koch Became An Oil Speculation Powerhouse," ThinkProgress, June 19, 2011. Accessed July 1, 2014.
- ↑ Lee Fang, "Not Just Goldman Sachs: Koch Industries Hoards Commodities as a Trading Strategy," The Nation, July 22, 2013. Accessed July 1, 2014.
- ↑ Asjylyn Loder, "Not Just Wall Street Opposes CFTC Derivatives Overhaul," Bloomberg Businessweek, April 15, 2010. Accessed July 1, 2014.
- ↑ Jump up to: 43.0 43.1 43.2 43.3 43.4 43.5 43.6 43.7 43.8 43.9 Nicholas Confessore, "Quixotic ’80 Campaign Gave Birth to Kochs’ Powerful Network," New York Times, May 17, 2014. Accessed May 29, 2014.
- ↑ Joel Brinkley, "Reagan Appoints Privatization Unit," New York Times, September 4, 1987. Accessed July 1, 2014.
- ↑ Robert Pear, "CLINTON'S HEALTH PLAN: Principles; Experts' Grades: 'A' in Security, 'C' in Simplicity, 'D+' in Savings," New York Times, September 24, 1993. Accessed July 1, 2014.
- ↑ Tim Dickinson, "Echoes of Philip Morris and Hillarycare," Rolling Stone, October 1, 2009. Accessed July 1, 2014.
- ↑ Americans for Prosperity Foundation, Directors, organizational website, accessed July 1, 2014.
- ↑ Chris Young, "Koch brothers, major corporations sponsor pension reform seminar for judges," Center for Public Integrity, April 25, 2014. Accessed June 30, 2014.
- ↑ Judicial Conference of the United States, Judicial Conference Policy on Judges' Attendance at Privately Funded Educational Programs, May 2006. Accessed June 30, 2014.
- ↑ Brendan Fischer, "Judge Who Halted Walker Dark Money Criminal Probe Attended Koch-Backed Junkets," The Progressive, May 27, 2014. Accessed June 30, 2014.
- ↑ Matea Gold and Tom Hamburger, "How Google worked behind the scenes to invite federal regulators to conferences," Washington Post, April 12, 2014. Accessed June 30, 2014.
- ↑ Nicholas Confessore, "Tax Filings Hint at Extent of Koch Brothers’ Reach," New York Times, September 12, 2013. Accessed July 1, 2014.